By
Professor Okanga Boniface
London, England, 6 January, 2025
In line with Microsoft IoT’s (2024) Video below, digital driven frugal innovation may also entail taking advantage of digital twin reflecting the advancement in artificial intelligence, robotics and machine learning technologies to introduce new products and operational processes that not only lower costs and improve affordability and accessibility of the previously unaffordable products, but also environmental sustainability
Frugal innovation is one of the disruptive game-changers of the 21st Century. It is a re-creator of the existing products that lowers costs to bolster a firm’s cost competitiveness. It is a re-creator of new points-of-difference that introduce unique novel selling propositions and differentiators to bolster a firm’s competitiveness. Frugal innovation inculcates a customer-centric business philosophy that prompts executives to ask difficult questions as to whether the business is doing the best to respond to the unfolding customer needs (Weiwei, 2024). This refocuses the business away from its existing less lucrative market segments to the more value generating segments. Unfortunately, combined with its inadvertent use by innovation ventures, the concept of frugal innovation does not also feature quite prominently in academic literature.
Given its value for leveraging innovation success, this implies frugal innovation is still one of the forgotten disruptive 21st Century’s strategic value creating resources. To respond to such epistemological gap, this seminal article highlights how frugal innovation drives cost competitiveness, creates unique points-of-differences, leverages a new product’s faster market diffusion, spawns operational efficiency, market growth, increases revenue, profitability and returns on shareholders’ value. Such approach is aimed at inspiring businesses to adopt more effective and clear frugal innovation strategies while researchers and academics also explore better ways of how innovation ventures can use frugal innovation to influence innovation success.
Without compromising quality, frugal innovation is a re-innovation process that emphasises the importance for re-evaluating and re-creating a costly complex product to render it simple, user friendly, sustainable, resource-saving and affordable by the designated target market. “Frugal” itself is an English word that requires sparing usage of resources in the way that eliminates wastage and costs.
As spiraling cost and standard of living continue to complicate life and humble even those in the developed markets just like poverty in the developing countries, frugal innovation introducing cheaper less complex quality products will continue to become an instrumental strategic value creating resource of the 21st Century. Customers will want cheap and cheaper better quality products. In response, businesses must also be able to consistently produce and deliver cheap and cheaper better quality products and services.
In such quests, frugal innovation becomes essential for enhancing simplicity, affordability, sustainability, resource optimization and efficient usage of the available products to meet the previously unmet needs. Frugal innovation is analogous to Kim and Mauborgne’s (2004) concept of “Blue Ocean Strategy”. Instead of engaging in the often costly competition, blue ocean strategy emphasises the importance of constant analysis and response to new unmet needs by creating and delivering products offering previously unanticipated values.
Frugal innovation emphasises the importance of not only creating new products, but also of re-evaluating the existing products to eliminate what customers do not need. Through such initiatives, businesses create and deliver products offering previously unanticipated values whilst also responding to the previously ignored needs. Faced with the challenges where traditional lending practices of banks ignored a large segment of poor consumers in Bangladesh, the creation of Grameen Bank as a solution represents a clear case of frugal innovation.
To respond to the credit needs of the poor that needed financing of various business ideas, Grameen Bank evaluated and identified gaps in the traditional banking system. Such gaps were arising from the ignored low-income borrowers without collaterals or well-defined history of credit worthiness.
As Company Compass’ (2024) video below indicates, this led to the creation of a collateral free lending model for the innovative but poor small businesses in rural Bangladesh. Of course with collateral free lending, risks of non-repayment of loans became more eminent. To insulate itself against such risks, Grameen Bank encouraged the formation of groups.
After the formation of groups that would be held accountable in the event of non-repayment, collateral free loans were then provided to most women groups in Bangladesh. This model became an instant success that subsequently diffused across Asia, Africa and South America. It disrupted the traditional bank’s lending business to small businesses.
Multitudes of micro-finance institutions sprung up to adopt the Grameen Bank’s collateral free lending model. In response, even small businesses that could qualify to get credits from the traditional financial institutions shifted to using credit facilities provided by micro-financial institutions emulating Grameen Bank’s collateral free lending model. This is because the lending approach introduced by Grameen Bank turned out to be simple, affordable and more responsive to the needs of poor consumers.
Just like Grameen Bank case insinuates, most products are often over engineered to render them less relevant for even the lucrative segments. In a bid to delight and improve customer attractions, most products are often over-engineered to create values that in some of the cases, most customers do not need. Attempts to create and offer the best for the market can instigate the creation of relatively more complex products that are not easy to use.
Such complexities often create new market gaps arising from customers who cannot easily use or afford the product. Complex products are often more costly and expensive as compared to less complex ones. It is often such a gap that frugal innovation aspires to fill by coming in to deconstruct, re-engineer and recreate the designated product and render it simple, easy to use and affordable to the hitherto larger excluded market segments (Radjou, 2024).
During innovation, market gap necessitating the importance for frugal innovation is often caused by most innovators’ quests to target highly rewarding premium market segments. Upon successful market launch of a new product, most innovators often seek to quickly generate higher returns so as to quickly recoup costs of innovation investments. In such quests, low income market segments are considered as less attractive and ignored.
Yet, just like in developing countries, most consumers around the world will continue to want cheap and cheaper less complex but quality products. Such trends and patterns of consumer behaviours will likely become the norm in the future to create new needs and market gaps. In effect, frugal innovation will become instrumental for responding to the needs of the depressed low income consumers in the developed countries whilst also doing the same for the poor in the developing countries.
Irrespective of their locations around the world, consumers will always want the cheapest best quality products. Michael Porter, the Harvard Strategy Professor told an Harvard audience in 1984 that it is only a firm which is able to produce and sell the best quality product at the lowest price that will gain a competitive edge. Today, 41 years after, the same business ideology still resonates with actual business realities and the understanding of even most of the most creative business executives.
Of course, market conditions in most developing countries and emerging markets like Brazil, India, China, Russia, United Arab Emirates, South Africa and most Eastern European countries are increasingly improving. Such improving conditions suggest premium pricing for premium quality can bolster a business’ effective market performance across the globe.
However, even with such positive developments, even the rich of the world will still want cheaper and cheapest best quality and easy to use products. That signifies frugal innovation shall remain relevant as one of the strategies for recreating the over-engineered and over-featured existing products to respond to the surging global needs for affordable and easy-to-use products.
Principles of Frugal Innovation
In such quests, most creative innovators as reflected in Figure 1, are increasingly using simplicity, affordability and resource-saving attributes as the differentiators for selling new versions of the existing products in new markets. This renders frugal innovation essential for improving the sale of affordable and simple easy-to-use new versions of the existing products to new market segments in developed and developing countries. Through frugal innovation, businesses able to tap enormous unfolding market opportunities in the developing countries.
Prahalad (2004) highlights such developing countries’ opportunities to constitute fortunes falling at the bottom of the global market pyramid. In his book titled: “The Fortune at the Bottom of the Pyramid: Eradicating Poverty Through Profits Hardcover”, Prahalad argues that as most innovative firms focus on creating products which are often more sophisticated and costly to respond to the complex needs in the developed countries, they tend to forget or even ignore the often mysteriously lucrative underdeveloped markets.
Prahalad reasons that developing countries could be poor to afford more complex and sophisticated costly products, but the tendencies of the general population to spend a dollar or two on a particular item often turn into a fortune that can influence the success of a business that focuses on identifying and satisfying such needs. To therefore tap the enormous unfolding opportunities in the developing countries that constitute the fortune at the bottom of the global market pyramid, businesses must not only produce for the sophisticated developed markets, but also strive to create simple, affordable and easy to use products (Mokter et al., 2022).
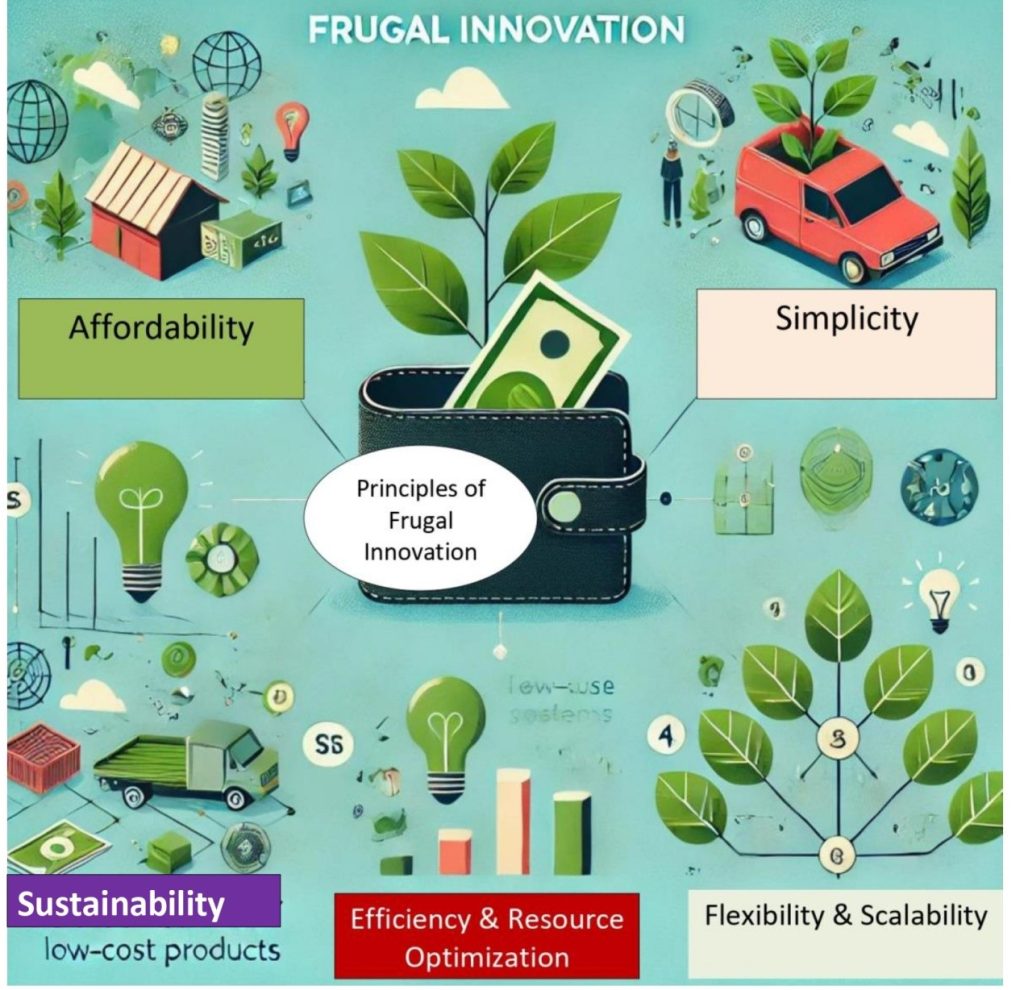
Image generated by Cloud Analytika using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Figure 1: Principles of Frugal Innovation
Innovation ventures must strive to create products that respond to the concerns and conditions in most of the developing countries. As innovation ventures respond to the needs in the developing countries, General Electric’s Portable ECG Machine case implies it also becomes easier for them to use such capabilities to catalyse their competitiveness in the developed markets. In terms of new product’s commercialization, this can improve new product’s faster diffusion. Frugal innovation increases a product’s market outreach. It extends a product lifecycle.
Frugal innovation recreates the existing product to de-escalate its complexity, unnecessary features, components, functionality and heftiness of its cost components. This reduces the product’s development and manufacturing costs to not only render the product easy to use, but also affordable to a majority of the poor global population.
Due to such idiosyncratic capabilities, frugal innovation has emerged as one of the unique strategic value creating resources. Frugal innovation which had hitherto been treated just as the strategy for responding to the needs of the consumers in poor countries is instead gaining momentum as one of the disruptive strategies of the 21st Century. As a disruptive strategy of the 21st Century, frugal innovation is displacing some of the established disruptive incumbents in the developed markets.
Consumers in the developed and developing markets are increasingly craving for affordable products to meet their strained budgets and easy to use products to save the increasingly scarce time. Such a view is echoed in AltexSoft’s (2024) video below, which indicates Ryanair as one of the most successful disruptive frugal innovators of the 21st Century.
Ryanair focused on analysing, identifying and eliminating what customers did not want or the most unnecessary costly products and services. It lowered the costs of air travel for every traveller. This improved the affordability, accessibility, efficiency and convenience of air travel. It bolstered its overall competitiveness and capabilities to disrupt the seamless operations of legacy airlines like British Airways, Lufthansa and Aer-Lingus.
Ryanair’s case insinuates frugal innovation eliminates gaps between the haves and the have-nots. This bolsters the seamless diffusion of the products which were previously made for the sophisticated developed markets to the majority of the poor and less sophisticated consumers in both the developed and the developing markets. From such insights, it is discernible that some of the incumbents that have been winners and are still winners are frugal innovators in one way or another.
When the likes of Toyota and Honda realised that the automobiles being produced by historicals like Ford and Daimler were not affordable to the majority of the global low income consumers, frugal innovation inadvertently or advertently became one of the business philosophies influencing their business thinking and operations to create less complex, simple to maintain, efficient and affordable cars.
Likewise in the early development of electrocardiogram (ECG) machines, higher costs limited affordability of the often more expensive electrocardiogram (ECG) machines. ECG machine’s higher costs meant the costs for heart diagnostics would also not slide down. To fill that gap, General Electric using its innovation from its Healthcare Division responded by diagnosing and recreating the existing ECG machines to create portable ECG machines (SmartHeart, 2023).
General Electric created a portable MAC-400 which uses battery for just $1000 as compared to the original heavy duty ECG machines that were being sold for $10,000. The portable MAC-400 became instrumental for improving the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular diseases in India.
The end result was that such frugal innovation model was widely adopted across the world as the strategy for lowering the cost and complexity of the functionality of ECG machines as well as the costs of heart condition diagnostics. Its business success influenced the likes of Apple to create Apple-Watch as well as John Hopkins Medicine to create and introduce portable ECG machines like Holter monitor which is privately used for monitoring heart conditions while far away from healthcare facilities (John Hopkins Medicine, 2024). This is reflected in the In-Depth Tech Reviews’ (2024) video below. It is from such insights that further research and innovations were undertaken to lower costs and render ECG machines more portable, simple to use, affordable and integrated with computers, Internet and smartphones
Using frugal innovation, Tata-Nano in India diagnosed the challenges that most Indian families face when adopting motorcycles as “family vehicles”. Such diagnosis influenced the creation of Tata-Nano that emerged as the world’s cheapest car sold for just $2500. Tata-Nano re-engineered the usual expensive cars to reduce complexity and costs of the components used as well as the used non-essential features.
Frugal innovation leverages new product’s market diffusion. It enables re-evaluation and recreation of the newly introduced products. This enables products that were not made for a certain market segment to be adopted and used by such market segments. Frugal innovation spawns the capabilities of businesses to rethink how the newly created product can be recreated to respond and serve the previously unanticipated needs. Such a view accentuates the notion that frugal innovation is the strategic process of re-evaluating and re-thinking how the existing products can be recreated to render it affordable and user-friendly for the previously ignored market segments.
In line with insights from Barney’s (1991) “Resource-based Theory” as well as analogy from Porter’s (1986) “Generic Competitive Strategies”, frugal innovation bolsters a firm’s competitiveness by creating and introducing new products to target new market segments. This improves a business’ growth and evolution in new markets. Frugal innovation improves the speed of a new product’s diffusion. It enables new product’s recreation. This aids the integration of new features, functionalities and attributes to bolster the acceptability of the product in new market segments.
Through frugal innovation, high performing businesses are often able to get customers who could have not tried the product to do so. This increases the rate of new product product’s adoption and diffusion. Frugal innovation enables a business try and experiment its new products with new market segments by trying different versions of the product. This enables innovation ventures discern the product version that best responds to the popular unfolding market demands and needs. Though using new product versions, it is often through such initiatives that frugal innovation leverages the new product’s faster diffusion from the developed markets to the developing markets.
It is only after Prahalad’s publication of his book-“The Fortune at the Bottom of the Pyramid” in 2004 that the significance of frugal innovation gained prominence amongst innovators and in academic studies and research. But analysis of pragmatic industry approaches implies the notion of frugal innovation did not start with Prahalad’s articulation in 2004. Instead the concept of frugal innovation is as old as the concept of new product development.
Historical Evolution of Frugal Innovation
In the pre-industrial revolution era, economic hardships and resource scarcity prompted most people to in one way or another become frugal innovators. Inadvertently or advertently, people often re-evaluated the existing ways of doing things to attempt to adopt and introduce the simplest, cost-effective and affordable ways of accomplishing the required activities. It is such inquisitiveness of exploring the better ways of doing things that instigated research and inventions leading to the introduction of major revolutionary inventions like Spinning Jenny, Steam Engine, Locomotives, Telegraph, Cotton Gin and Assembly Manufacturing Technology by Ford.
However, as machineries and new technologies introduced during and post the industrial revolution eras lowered costs and simplified the ways of doing things, it also induced certain unintended consequences that motivated the evolution of the concept of frugal innovation.
Industrial revolution and its post technological advancements instigated the emergence and subsequently increment of affluent middle class working population. This population segment represented the growing lucrative market segment that required the best products and services. In response, innovators also explored the best ways of tapping such opportunities by creating and introducing the best machines and technologies.
Using the best machines and technologies, businesses were able to produce and deliver the best to the growing sophisticated middle class population. However, in the process, the intense usage of more advanced machines, technologies and the adopted computer technologies caused over-engineering that increased the complexity of certain products as innovators strove to create and offer the best for the market.
The case of complexly designed and engineered Blackberry Phones as was displaced by Apple’s iPhones indicates such complex products that became the source of inconveniences and higher costs. This unaffordability and lack of ease of use discouraged certain market segments or even the affluent middle class individuals unwilling to spend so much on a product which is supposed to be just a simple one.
In the developed markets, the emergence of such behaviours created new market gaps that inspired frugal innovators to engage in product simplification as the strategy for responding to the needs ignored by complex products. Yet as they did, innovators adopting frugal innovation were not only able to respond to the needs of the dissatisfied middle class population, but also the lower income market segments of the world.
Frugal innovation is part of the continuous innovation and improvement strategy. After the market introduction of a new product, it is frugal innovation that enables a business re-evaluate its products in the context of new customer insights and the emerging new competition dynamics.
Through such analysis, innovation ventures become able to discern the improvement initiatives that must be adopted to improve the further market diffusion of the product. Failure to undertake frugal innovation aimed at simplifying a complex product to improve its affordability and appeal to customers does not only explain the failure in the commonly cited Blackberry Phone Case.
Instead it also illustrates the incidents reflecting lack of inculcated innovation culture that caused HTC’s failure. As illustrated in the Rise and Fall Documentaries’ (2024) video below, HTC, an incumbent smartphone maker that had gained significant market share in the late 1990s when Apple was still researching and experimenting its smartphone concepts, failed to defend its market position when competition heightened in the late 2000s.
After the initial success, HTC abandoned continuous innovation and improvement which required the use of frugal approach to render its smartphone concepts further affordable and simple to use. The effect is that when the likes of disrupters like Apple and Samsung finally entered the market with more easy to use and relatively affordable smartphones, it did not take long before HTC’s market share begun to slump. Even if HTC still continues to produce smartphones, its failure to fight back left it relegated to the periphery of the global smartphone manufacturing industry.
Even if the concept of frugal innovation does not feature much in the innovation and entrepreneurial venture development literature, such insights signify the extent to which frugal innovation is the forgotten disruptive 21st century’s strategic value creating resource. Frugal innovation is a disruptive strategic value creating resource that spawns a firm’s sustainable competitive advantage. It unleashes revolutionary thinking and concepts that completely change and transform how humans live life. As reflected in Jugaad innovation case, it was the quests for the adoption of simple and cost-effective problem-solving approaches that inspired the emergence of Jugaad Innovation as a resource-constrained problem-solving approach in India.
In Japan, the need for cost-effective simple operational approach instigated the introduction of Toyota Production System as well as Lean Operational Approaches. Motorola’s Six-Sigma Operational Business Philosophy was also a frugal process innovation aimed at reducing wastes, costs and operational glitches that affect the simplicity of operational processes.
As innovators introduce new products, frugal innovation has emerged as one of the rethinking methodologies that enable a business question whether what is created and delivered is the best for meeting the existing customer needs. It is an out-of-the box thinking approach that enables innovators come up with the best alternative versions of the existing products.
Frugal innovation enables a business access untapped markets, gain cost leadership, adopt flexible and scalable operational approach, embrace innovation culture and mitigate risks. As depicted in Motorola’s Six-Sigma case, frugal innovation does not only improve the attractiveness of a product, but also processes through which various products are made.
When Motorola wanted to lower the costs of its products, it was frugal innovation that drove the questioning and re-evaluation of its existing business processes. As depicted in Knowledge Factory’s (2024) video on Six-Sigma, this influenced the emergence of the concept of Six-Sigma as the process control methodology for statistically analysing and reducing wastes and costs associated with the identified manufacturing processes
In line with Ansoff’s (1967) “Product-Market Matrix”, this enhances a firm’s growth on all dimensions. Frugal innovation leverages the efficacy of market penetration, market development, product development and diversification strategies.
Through market penetration, Figure 2 implies frugal innovation creates cheaper simplified versions of the existing complex products to bolster their diffusion in the existing markets. Market development of the business is enhanced when frugal innovation creates or modifies new versions of the existing products to respond to the needs of the previously ignored market segments.
Product development is improved when frugal innovation prompts businesses to ask difficult questions that introduce new disruptive products to bolster the business’ performance in the existing market, whilst also extending the product lifecycle of the existing products.
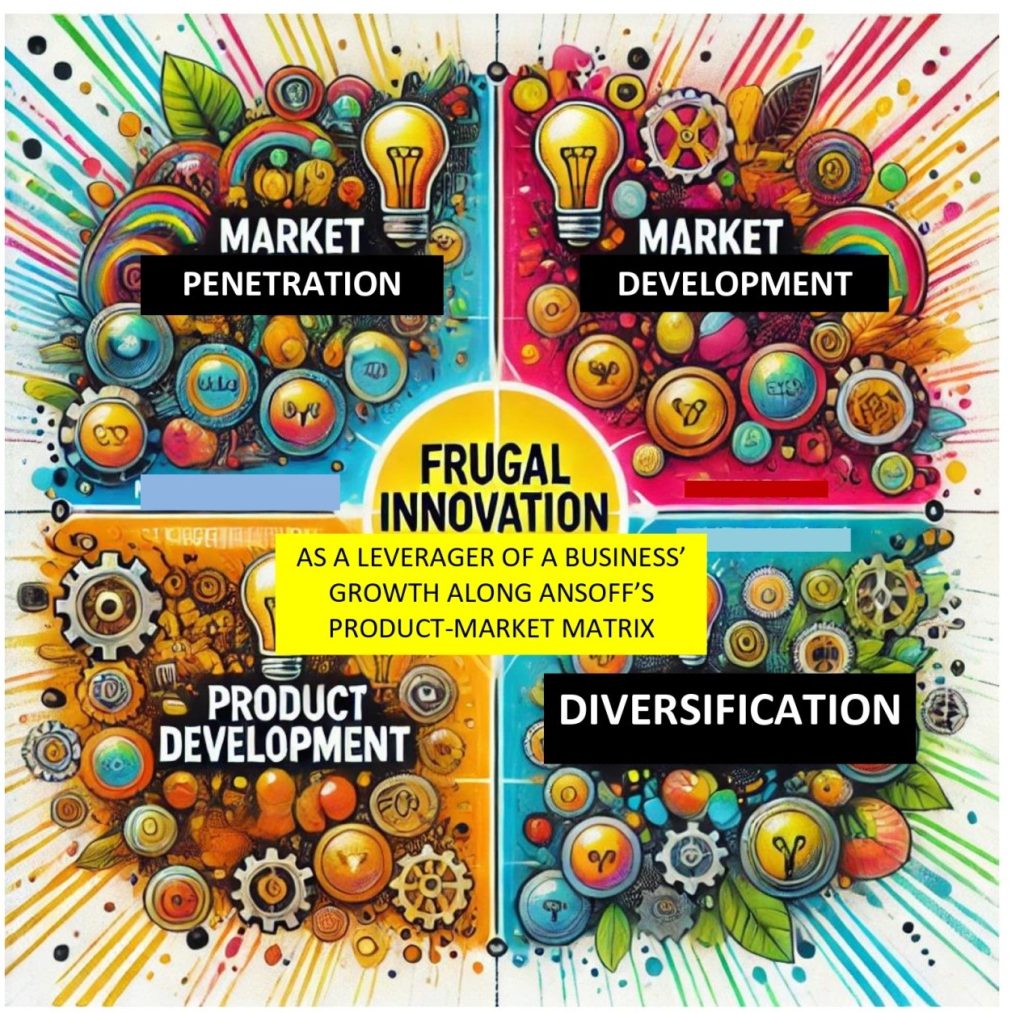
Figure 2: Frugal Innovation as a Leverager of a Business’ Growth along Ansoff’s Product-Market Matrix
By creating additional versions of the existing products, frugal innovation enhances a firm’s diversification to create a range of product portfolios that mitigate risks of market failures.
Frugal Innovation Strategies
However, achievement of such positive outcomes may require frugal innovation initiative to use a combination of innovation strategies encompassing:
- Resource-driven Frugal Innovations
- Cost-driven Frugal Innovations
- Need-based Frugal Innovations
- Reverse-driven Frugal Innovations
- Sustainability-driven Frugal Innovations
- Jugaad Frugal Innovations
- Process-driven Frugal Innovations
- Digital-driven Frugal Innovations
- Socially-driven Frugal Innovations
- Modular Frugal Innovations
- Hybrid Frugal Innovations
- Inclusive Frugal Innovations
Resource-driven frugal innovation is an initiative that focuses on minimizing the amount of materials used in the manufacturing process. To reduce energy usage and costs, Chotu-Kool Refrigerator is created to use thermoelectric cooling system as a substitute for compressor usage.
Cost-driven frugal innovation focuses on analysing and reducing costs throughout the value chain system in order to create cheaper versions of the existing products. Such approach is reflected in Unilever Sachet Products that not only adopt low costs, but also single-use packaging for detergents and shampoos meant for targeting low-income market segments. Need-based frugal innovation aims to respond to the most pressing needs ignored by the existing market operators.
As the operators in the global energy segment ignored the lucrative solar energy market in Africa, M-KOPA Solar adopted need-based frugal innovation to create and offer solar package for off-grid consumers in Africa. Reverse-driven frugal innovation refers to innovation created for the resource-constrained markets in developing countries that later turn out to be as well quite attractive to the consumers in the developed markets.
When General Electric Healthcare introduced a cheaper Portable ECG Machine (MAC400) to solve healthcare diagnostic crisis in India, it didn’t know that the product would turn into a disrupter in the US and European healthcare diagnostic market. Sustainability-driven frugal innovation focuses on adopting ecologically friendly business approaches and products like Solar Water Pumps and Fairphone as a way of minimizing resource wastage.
Jugaad frugal innovation uses simple, affordable and efficient products and approaches as the way for responding to the needs of the grassroot consumers in resource-constrained societies. In rural India, such initiatives are depicted in the adoption of Mitticool which is a non-electric refrigerator made from clay and the use of bicycle-water driven pumps.
Process-driven frugal innovation improves process efficiency to unlock cost advantages that bolster the product’s competitiveness. Such initiative was adopted by Ryanair that invested heavily in process efficiency improvement to reduce wastes, lower costs and create low cost airline operation.
Digital-driven frugal innovation focuses on using the available digital technologies as well as AI and machine learning technologies to create and deliver simple, efficient and affordable products. Such frugal innovation approaches are reflected in the introduction of fintech companies’ initiatives introducing services like digital credits by Nubank in Latin America, M-Pesa by Safaricom in Kenya and MTN Mobile Money by MTN in Africa. As a result of digital frugal innovation in the financial sector, Silicon Valley Innovation Center’s (2020) video below suggests it is only traditional financial institutions that are able to assimilate and counter fintech companies that will emerge as winners in the 21st Century.
Socially-driven frugal innovation uses corporate social responsibility as the main strategy for improving the quality of life whilst also marketing and promoting the business or the product. As LifeStraw focuses on delivering clean water for those without access to clean water as revenue generating initiative, Grameen Bank uses a frugal microfinance model that focuses on providing small loans to low-income market segments.
In contrast, modular frugal innovation focuses on creating and delivering products that are easy to use, modify, change, upgrade, repair, maintain and improve without distorting its original design and functionality. When Toyota, the automaker first followed the likes of Ford into the global car-making industry, it used modular frugal innovation to create and deliver easy to maintain, repair, cost-efficient and fuel-efficient cars. It was such approach that created unique selling propositions that enable Toyota upto to today to remain a disrupter and leader in the global car-making industry.
Hybrid frugal innovation strives to lower costs to improve affordability whilst also using advanced features to improve the overall functionality and efficacy of the product. Most smartphones remain expensive to compensate for the advanced features used. To displace rivals like Apple’s iPhones, Samsung uses hybrid frugal innovation to ensure it creates and delivers smartphones with more disruptively advance features for relatively lower prices.
Inclusive frugal innovation emphasises the creation of products that not only respond to the larger market segments, but also to the needs of the marginalized and ignored market segments. To lower the costs of eye cataract surgeries in rural poor India, Aravind invented the model that lowered costs to provide affordable eye cataract surgeries across India.
As this model proved effective among the poor in India, it was also widely adopted by the middle income consumers and the rich across India and the world. In otherwords, all these imply despite its advertent or inadvertent use by businesses, frugal innovation is one of the game-changing strategies of the 21st Century. However, given its less prominence in academic literature, it seems frugal innovation still remains the forgotten disruptive 21st Century’s strategic value creating resource. To fill such epistemological gap, more current and future studies must continue to focus on exploring the principles, strategies and methodologies for improving effective use of frugal innovation as one of the disruptive strategic value creating resources of the 21st Century.
Citation: Okanga, B. (2025). Frugal Innovation: The Forgotten Disruptive 21st Century’s Strategic Value Creating Resource. London: Cloud Analytika.
Further Readings:
AltexSoft. (2024). Youtube Video: Ryanair: Flying High on a Budget. Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uno5Ua6M8pI
Ansoff, H.I. (1957). Strategies for Diversification. Boston: Harvard Business Review. https://archive.org/details/strategiesfordiversificationansoff1957hbr
Company Compass. (2024). Youtube Video: How Grameen Bank Changed the Lives of the Poor. Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o8GAa5tNwIM
In-Depth Tech Reviews. (2024). Youtube Video: Wellue Pulsebit EX ECG/EKG Tracker Review – Better Than Smartwatches. Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8-3lCg8kJmQ
Company Compass’ (2024) YouTube Video: How Grameen Bank Changed the Lives of the Poor: Youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o8GAa5tNwIM
John Hopkins Medicine. (2024). Holter Monitor: Cardiovascular Heart and Vascular Diagnosis and Screening for Cardiovascular Conditions Angiogram What is a Holter monitor? New York: John Hopkins: University. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/holter-monitor#:~:text=A%20Holter%20monitor%20is%20a,used%20to%20check%20the%20heart
Kim, W.C., & Mauborgne, R. (2004). Blue Ocean Strategy. Boston: Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2004/10/blue-ocean-strategy.
Knowledge Factory. (2024). Youtube Video: Six Sigma: A Brief History. Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UO2EQpwGu6E
Microsoft IoT. (2024). Youtube Video: Building Digital Twins, Mixed Reality and Metaverse Apps. Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GAkB98ewcjI/ 2:46.
Mokter, H., Agarwal, N., Bhatti, Y., & Levänen, J. (2022). Frugal innovation: Antecedents, mediators, and consequences. Creativity & Management, 31(3), 521-540. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/caim.12511
Prahalad, C.K. (2004). The Fortune at the Bottom of the Pyramid: Eradicating Poverty Through Profits Hardcover. New York: Pearson. https://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/the-fortune-at-the-bottom-of-the-pyramid-eradicating-poverty-through-profits/
Radjou, N. (2024). Frugal innovation: 3 principles to help improve food production. New York: World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/05/frugal-innovation-3-principles-to-help-improve-food-production/
Rise and Fall Documentaries. (2024). Youtube Video: Why HTC Phones Failed: The Rise and Fall of a Smartphone Giant. Link- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f8K2yq82zYQ
Silicon Valley Innovation Center. (2020). Youtube Video: The New Wave Of FinTech: The End Of Banking. Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3UA4CZW689Q
SmartHeart. (2023). A Brief History of the ECG Machine: From Inception to Now. https://getsmartheart.com/blogs/news/a-brief-history-of-the-ecg-machine-from-inception-to-now?srsltid=AfmBOooDRrVscCHW0U2LSF5kBuXh3LYX5cnI1XQ8c24jTqKEwzqRs-rg
Weiwei, Q. (2024). How to unleash frugal innovation through internet of things and artificial intelligence: Moderating role of entrepreneurial knowledge and future challenges. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 202(1), 123-138. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162524000829











